What Is Acupuncture?

Acupuncture is an effective form of medical treatment that has evolved into a complete holistic health care system. Practitioners of acupuncture and Chinese medicine have used this non-invasive treatment method to help millions of people become well and stay well.
Acupuncture promotes natural healing. It can enhance recuperative power and immunity, support physical and emotional health, and improve overall function and well-being. It is a safe, painless and effective way to treat a wide variety of medical problems.
What Is Qi?
According to Classical Chinese Philosophy, Qi (pronounced “chee”), or vital energy, is the force that makes up and binds together all things in the universe. Qi flows throughout the body. Qi animates the body and protects it from illness, pain and disease. Consequently, the quality, quantity and balance of Qi significantly influence a person’s health.
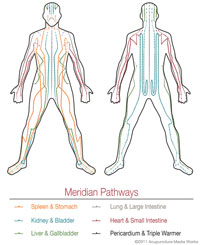
How Does Qi Move?
Qi flows through specific pathways called meridians. There are fourteen main meridians inside the body. The diagram shows the meridian pathways in the body. Each of these is connected to specific organs and glands.
Meridian pathways are like rivers flowing inside the body. Where a river flows, it transports life-giving water that provides nourishment to the land, plants and people. Similarly, where meridian pathways flow, they bring life-giving Qi.
How Is Qi Disrupted?
An obstruction to the flow of Qi is like a dam. When Qi becomes backed up in one part of the body, the flow becomes restricted in other parts. This blockage of the flow of Qi can be detrimental to a person’s health. This blockage or stagnation cuts off vital nourishment to the body, organs and glands.
Emotional trauma, stress, excessive activities, physical or accident injury, lack of exercise, overexertion, seasonal changes, or poor diet are among the many things that can influence the quality, quantity and balance of Qi.
Normally, when a blockage or imbalance occurs, the body easily bounces back, returning to a state of health and well-being. However, when this disruption is prolonged or excessive, or if the body is in a weakened state, illness, pain, or disease can set in.
Blockage of the flow of Qi can be detrimental to a person’s health and leads to various signs and symptoms or health concerns.
What Does an Acupuncturist Do?
During the initial exam, your Fairfax acupuncturist takes a full health history. In addition to physical exam, he may ask questions regarding health, symptoms and lifestyle. He may also conduct an appropriate Oriental Medicine evaluation including pulse and tongue diagnosis.
Gathering this information enables the practitioner to effectively diagnose and detect any specific imbalances of Qi that may have contributed to a person’s health problems. Your acupuncturist can then create a well-structured treatment plan.
Once the imbalances of Qi are detected, an acupuncturist will place fine, sterile needles at specific acupuncture points along meridian pathways. This safe and painless insertion of the needles can unblock the obstruction and balance Qi where it has become unbalanced. Once acupuncture unblocks obstruction, Qi can freely circulate throughout the body. As a result, it provides adequate nourishment to cells, organs, glands, tissues and muscles. This can eliminate pain and restore balance and harmony, as well as the body’s ability to heal itself—ultimately leading to optimal health and well-being.
Acupuncture and Chinese medicine are safe, effective and drug-free therapies that can help address a wide variety of common ailments and problems.
Benefits of Acupuncture Treatment
Acupuncture is recognized by leading national and international health organizations to be effective in the treatment of a wide variety of medical problems.
- Adverse reactions to radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy
- Abdominal pain (in acute gastroenteritis or due to gastrointestinal spasm)
- Allergic rhinitis (including hay fever)
- Bell’s palsy
- Cancer pain
- Chronic gastritis
- Diabetes mellitus, non-insulin-dependent
- Dysmenorrhoea
- Earache
- Facial pain
- Female infertility
- Fibromyalgia and fasciitis
- Headache
- Hypertension
- Induction of labor
- Insomnia
- Knee pain
- Leukopenia
- Low back pain
- Male sexual dysfunction, non-organic
- Malposition of fetus
- Morning sickness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Neck pain
- Obesity
- Osteoarthritis
- Pain in dentistry
- Peptic ulcer
- Periarthritis of shoulder
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Postoperative pain
- Premenstrual syndrome
- Prostatitis
- Raynaud syndrome
- Renal colic
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Sciatica
- Sore throat (including tonsillitis)
- Spine pain, acute
- Sprain
- Stroke
- TMJ dysfunction
- Tennis elbow
- Ulcerative colitis, chronic
- Urine retension, traumatic






